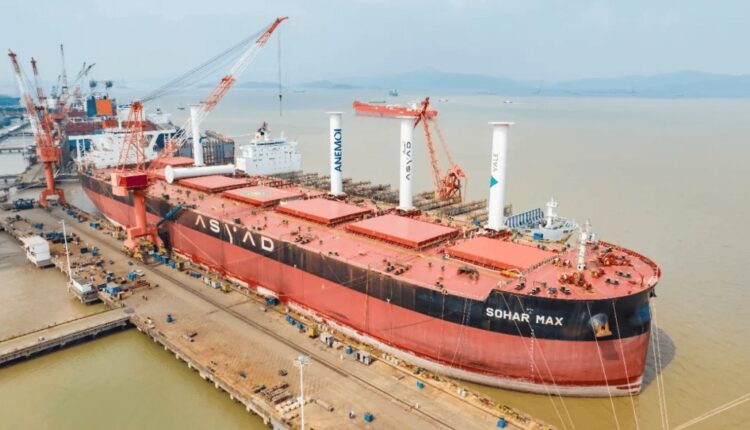
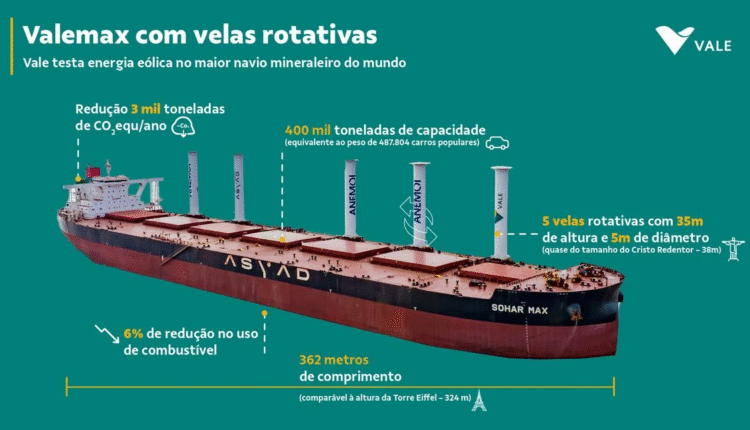
Sea News – International Desk- The global maritime industry is witnessing a new wave of innovation. In the Port of Sohar, Oman, the logistics group Asyad has unveiled the Sohar Max—a next-generation vessel equipped with five rotor sails that pave the way toward a more sustainable future for seaborne transport. This cutting-edge technology, which harnesses wind power to reduce fuel consumption, not only addresses environmental challenges but also presents opportunities for countries like Iran to engage with global innovation trends. As the world shifts toward carbon reduction, this ship could serve as a model for the future of maritime trade.
What Are Rotor Sails?
Rotor sails are tall, cylindrical structures installed on a ship’s deck that convert wind energy into thrust through controlled spinning. Based on the Magnus effect—a principle of fluid dynamics describing the pressure differential created when a spinning object moves through air or liquid—these rotating cylinders generate lateral force that propels the vessel forward.
Each rotor sail on the Sohar Max stands approximately 25 meters tall and 4 meters in diameter, constructed from aluminum or marine-grade composite materials. The cylinders rotate at speeds between 150 and 250 revolutions per minute, powered by low-energy electric motors (50–100 kW). Smart sensors adjust their rotational speed in real time based on wind conditions. This system can reduce diesel fuel consumption by 20–30%. For example, a ship equipped with five rotor sails can save up to 2.2 million liters of fuel annually and cut carbon dioxide emissions by up to 6,000 tonnes—making rotor sails a highly attractive option for commercial shipping fleets.
Environmental and Economic Benefits
Shipping accounts for more than 80% of global trade and is one of the largest contributors to greenhouse gas emissions. According to the International Maritime Organization (IMO), the industry must reduce its carbon emissions by 50% by 2050. The rotor sail technology showcased on the Sohar Max represents a tangible step in that direction. By reducing fuel consumption, it not only cuts emissions but also decreases the risk of oil and chemical pollution in oceans—critical for marine ecosystems.
From an economic standpoint, this technology significantly reduces operational costs. Annual fuel savings can amount to hundreds of thousands of dollars per vessel, especially on long-haul routes between Asia, Europe, and the Americas. As demand for green technologies grows, shipping companies adopting rotor sails may also qualify for international financial incentives and tax exemptions.